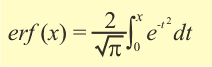Material Properties: Kevlar 49 (Composite)
Data Available:
- Thermal Conductivity
Thermal Conductivity |
|
| UNITS | W/(m-K) |
| a | -2.65 |
| b | 1.986637 |
| c | 1.24851 |
| d | 0.57 |
| e | -8 |
f |
0.777857 |
data range |
6-302 |
equation range |
0-350 |
curve fit standard error relative to data |
7.4 |
Has equation of the form: |
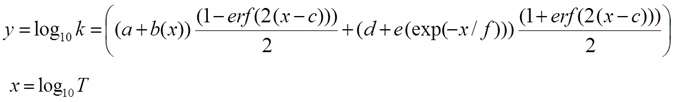 |
Therefore k Solves as: |
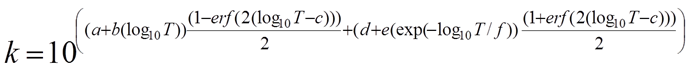 |
Where: Coefficients a – f are summarized in the table, T is the temperature in K (x-axis), and y is Thermal Conductivity (k) to solve for. "erf(x)" is the Gauss error function and "exp()" is the exponential.
NOTE: The error function (sigmoid shape) is used to blend fits over separate temperature ranges.
The error function ‘erf(x)’ (also known as the Gauss error function) is defined as:
(When x is negative, the integral is interpreted as the negative of the integral from x to zero.) In Excel the error function may be calculated by employing the following format ‘ERF( lower_limit, upper_limit)‘ or simply ‘ERF(value of x)‘. For example ERF(0, 1.5) = ERF(1.5) which results in the integral of error function between 0 and 1.5. Excel 2010 and later evaluate correctly for both possitive and negative values of x. Whereas earlier versions can only evaluate for positive values of x (ie x > 0). Thus one must employ –ERF(x) = ERF(-x) to evaluate negative values of x properly in earlier versions of Excel (prior to 2010). |