VLE Thermodynamic Consistency: Point Test background
Test 3: Point Test (Differential Test). The Point Test was first introduced by Kojima and coworkers:19,22
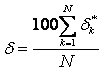 ,
,
where 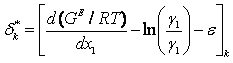 .
.
d*k represents the deviation for individual experimental points, d represents an overall deviation in percent, and e is defined in the Herington Test background. As noted for the Herington test, the value of e cannot be neglected for isobaric data sets. To avoid complexities associated with HE data sets, the Point Test was not applied to isobaric data sets. The values of g1, g2 are first calculated from the experimental values of T-p-x-y data.
The calculated values of
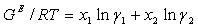 are fitted by use of a Pade approximation for the activity coefficient, shown here.
are fitted by use of a Pade approximation for the activity coefficient, shown here.

In this research, M = 1 and N = 3. This expression reduces to the Redlich-Kister expansion when M = 0. The quantityd*k is determined with the slope of the fitted Pade approximation and calculated values of 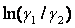 . The criteria given by Kojima and coworkers19,22 are that if d < 5, the VLE data set passes the test, otherwise it fails.
. The criteria given by Kojima and coworkers19,22 are that if d < 5, the VLE data set passes the test, otherwise it fails.
The quality factor for the Point Test can be calculated with the overall percent deviation of the slope:
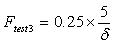 , with the limits:
, with the limits: 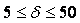 .
.
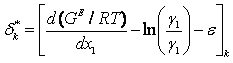 .
.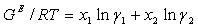 are fitted by use of a Pade approximation for the activity coefficient, shown here.
are fitted by use of a Pade approximation for the activity coefficient, shown here.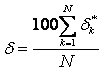 ,
,
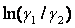 . The criteria given by Kojima and coworkers19,22 are that if
. The criteria given by Kojima and coworkers19,22 are that if 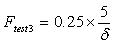 , with the limits:
, with the limits: 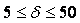 .
.